Con la llegada del 2017, una de las tantas decisiones fue que no ibamos a escribir más artículos en ingles, por lo tanto queremos adecuar todas las categorías (o tags) del sitio web, al español.
Nueva organización de tags en Consultoria-SAP
Con la llegada del 2017, una de las tantas decisiones fue que no ibamos a escribir más artículos en ingles, por lo tanto queremos adecuar todas las categorías (o tags) del sitio web, al español.
Intra and Cross Company-Codes Stock Transfer Posting
Stock Transfer Posting between plants in a same company code
- If the material transferred between plants is not-valuated material ("value update indicator" is not set in the material type configuration for the plants), the stock transfer posting does not affect accounting.
- If the material is valuated for the plants where stock transfer posting occurs and the valuation level is company code, stock transfer posting also does not affect accounting. It's because the value of a certain material in all plants in the company code is the same.
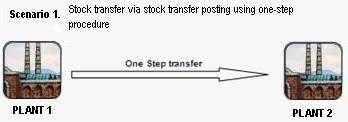
- If the material is valuated for the plants where stock transfer posting occurs and the valuation level is plant, stock transfer posting will affect accounting.If the procedure used is one-step transfer posting, the transaction will create accounting journals when it's posted. The inventory account in the issuing plant will be credited and the one in the receiving plant will be debited.If the procedure used is two-steps transfer posting, the "Remove from Storage" transaction will create accounting journal when it's posted. The inventory account in the issuing plant will be credited, and the one in the receiving plant will be debited (although in term of quantity it's still on "stock in transfer" in the receiving plant, not in "unrestricted-stock" yet).
The "Place in Storage" transaction will not create accounting journal as it only transfers "stock in transfer" to "unrestricted-stock" in the receiving plant (in a same plant).
Procedures of Stock Transfer Posting between plants
SAP One-step and two-steps stock transfer posting procedures
SAP FI: Clear G/L Account
Clear G/L Account (F-03):
"The following are differences between clearing accounts function and posting with a clearing transaction or posting with a payment:• A document header don’t need to be enteredClearing accounts function can be used to clear debits and credits that balance to zero (for example, invoices and payments that have already been entered).
• You can only clear open items from one account
Since internal transfer postings may have to be generated, a document type must be defined for clearing in customizing by selecting the activity Define Posting Keys for Clearing in the Implementation Guide for Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable.
The Maintain Accounting Configuration: Clearing Procedures – List screen appears. Select the Transfer Posting with Clearing transaction. A detailed screen appears. For each account type, you can specify a default document type to be used for posting a clearing document (if this is required for the clearing transaction).
Why Back Up the Database
Split-Mirror Backup
Why Back Up the #SAP's Database?For large global organizations spanning operations in many countries, a robust Information Technology Infrastructure supporting 24x7 365 days a year has become absolutely necessarily. Non-availability of Information Systems for however short time would cause these organization losses in Millions. The loss of Data due to system failures would even result in closure of these organizations. In such a scenario it is become absolutely necessary to not only have a mechanism to efficiently take Backup of the systems but also to be able to do it without any downtime and performance degradation.
The Split-Mirror technology helps in achieving High Availability of Database, by letting a system quickly take backup, typically in seconds, and it also helps in eliminating the use of System Resources of the Database Server for backing up the database, thus efficiently avoids System degradation (often experienced) while Backups are running.
SAP Advanced Delivery Management
SAP Advanced Delivery Management
An overview presentation of SAP Advanced Delivery Management: a new way of implementing SAP Solutions. View Document More info:Authorization Objects for ALE EDI
Object ALE/EDI: Maintaining logical systemsAuthorization B_ALE_LS_ALL
————————————————————————-
| Field Values
| Logical system
| *
————————————————————————-
Object ALE/EDI: Distributing master dataAuthorization B_ALE_MA_ALL
————————————————————————-
| Field Values
————————————————————————-
| Logical message type
| *
————————————————————————-
SAP BusinessObjects Predictive Analysis
SAP BusinessObjects Predictive Analysis
Transforming the Future with Insight Today
What if …- . . . You could identify hidden revenue opportunities within your customer base through predictive analytics?
- . . . You could retain your high-value customers/employees/vendors/partners with the right retention offers?
- . . . Your call center agents could delight customers with the best next-step recommendations?
- . . . You could increase cross-sell and up-sell effectiveness through cross-channel coordination?
- . . . You could build long-term customer/employee/vendor/partner relationships with intelligent interactions?
Please read this exceptional document: Predictive Analysis Overview
SAP: Stock Transfer between plants
Stock Transfer from a plant to another plant in SAP – Intra Company and Cross-Company Codes
For some reasons, we may need to transfer stock from one plant to another plant. In SAP ERP, it can be done using several procedures. Each procedure is different with others and may fit with a certain situation or business requirement. In this post I will explain about the procedures of how to transfer stock between plants in SAP ERP, so you can choose the best procedure according to your business requirement.In SAP ERP, stock transfer from one plant to another plant can be done through:
SAP default text editor
How to activate or deactivate MS-Word as default text editor
When you want to activate/deactivate MS Word as the text editor for SAPscript/Smartforms.- Call transaction se38, enter program RSCPSETEDITOR and press Execute (F8). On the next screen, select the checkbox SAPScript/Smartforms and press ‘Activate’.
- This is a fantastically fast method to produce multiple texts in multiple languages provided they are supported by your code page. Check out the OSS note below for comprehensive instructions on MS Word setup and available options.
OSS Note: 742662.
SAP FI Tables and Fields
Financial Accounting
| Financial Accounting | ||
|---|---|---|
| Table Name | Description | Important Fields |
| FBAS | Financial Accounting “Basis” | |
| BKPF | Accounting Document Header | BUKRS / BELNR / GJAHR |
| BSEG | Accounting Document Segment | BUKRS / BELNR / GJAHR / BUZEI |
| BSIP | Index for Vendor Validation of Double | BUKRS / LIFNR / WAERS / BLDAT / |
| Documents | XBLNR / WRBTR / BELNR / GJAHR / BUZEI | |
| BVOR | Inter Company Posting Procedure | BVORG / BUKRS / GJAHR / BELNR |
| EBKPF | Accounting Document Header (docs from External Systems) | GLSBK / BELNR / GJHAR / GLEBK |
| FRUN | Run Date of a Program | PRGID |
| KLPA | Customer / Vendor Linking | NKULI / NBUKR / NKOAR / PNTYP |
| / VKULI / VBUKR / VKOAR | ||
| KNB4 | Customer Payment History | KUNNR / BUKRS |
| KNB5 | Customer Master Dunning Data | KUNNR / BUKRS / MABER |
| KNBK | Customer Master Bank Details | KUNNR / BANKS / BANKL / BANKN |
| KNC1 | Customer Master Transaction Figures | KUNNR / BUKRS / GJHAR |
| KNC3 | Customer Master Special GL Transactions Figures | KUNNR / BUKRS / GJAHR / SHBKZ |
| LFB5 | Vendor Master Dunning Data | LIFNR / BUKRS / MABER |
| LFBK | Vendor Master Bank Details | LIFNR / BANKS / BANKL / BANKN |
| LFC1 | Vendor Master Transaction Figures | LIFNR / BUKRS / GJHAR |
| LFC3 | Vendor Master Special GL Transactions Figures | LIFNR / BUKRS / GJHAR / SHBKZ |
| VBKPF | Document Header for Document Parking | AUSBK / BUKRS / BELNR / GJHAR |
| FBASCORE | Financial Accounting General Services “Basis” | |
| KNB1 | Customer Master (Company Code) | KUNNR / BUKRS |
| LFA1 | Vendor Master (General Section) | LIFNR |
| LFB1 | Vendor Master (company Code Section) | LIFNR / BUKRS |
| SKA1 | G/L Account Master (Chart of Accounts) | KTOPL / SAKNR |
| SKAT | G/L Account Master (Chart of Accounts Description) | SPRAS / KTOPL / SAKNR |
| MAHNS | Accounts Blocked by Dunning Selection | KOART / BUKRS / KONKO / MABER |
| MHNK | Dunning Data (Account Entries) | LAUFD / LAUFI / KOART / BUKRS / |
| KUNNR / LIFNR / CPDKY / SKNRZE / | ||
| SMABER / SMAHSK / BUSAB | ||
| FI-GL-GL (FBS) | General Ledger Accounting: Basic Functions- G/L Accounts | |
| SKAS | G/L Account Master (Chart of Accounts Key Word list) | SPRAS / KTOPL / SAKNR / SCHLW |
| SKB1 | G/L Account Master (Company Code) | BUKRS / SAKNR |
| FI-GL-GL (FBSC) | General Ledger Accounting: Basic Functions - R/3 Customizing for G/L Accounts | |
| FIGLREP | Settings for G/L Posting Reports | MANDT |
| TSAKR | Create G/L account with reference | BUKRS / SAKNR |
| FI-GL-GL (FFE) | General Ledger Accounting: Basic Functions - Fast Data Entry | |
| KOMU | Account Assignment Templates for G/L Account items | KMNAM / KMZEI |
| FI-AR-AR (FBD) | Accounts Receivable: Basic Functions - Customers | |
| KNKA | Customer Master Credit Management: Central Data | KUNNR |
| KNKK | Customer Master Credit Management: Control Area Data | KUNNR / KKBER |
| KNKKF1 | Credit Management: FI Status data | LOGSYS / KUNNR / KKBER / REGUL |
| RFRR | Accounting Data – A/R and A/P - Information System | RELID / SRTFD / SRTF2 |
| FI-BL-PT | Bank Accounting: Payment (BFIBL_CHECK_D) Transactions – General Sections | |
| PAYR | Payment Medium File | ZBUKR / HBKID / HKTID / RZAWE / |
| CHECT | ||
| PCEC | Pre-numbered Check | ZBUKR / HBKID / HKTID / STAPL |
| FI-BL-PT-AP(FMZA) | Bank Accounting: Payment Transactions – Automatic Payments | |
| F111G | Global Settings for Payment Program for Payment Requests | MANDT |
| FDZA | Cash Management Line Items in Payment Requests | KEYNO |
| PAYRQ | Payment Requests | KEYNO |
What is the table name for G/L Master data, when we create centrally (T.Code - FS00)?
As far as general ledger master data is concerned, the following tables are involved :
Table name : SKB1 : G/L Account Master ( Company Code)
Fields:
BUKRS : Company Code
SAKNR : G/L Account
Table name : SKA1 : G/L Account Master ( Chart of Accounts )
Fields:
KTOPL : Char of Accounts
SAKNR : G/L Account
Table name : SKAT : G/L Account Master Record ( Chart of Accounts : Description )
Fields:
SPRAS : Language
KTOPL : Char of Accounts
SAKNR : G/L Account
*-- Viji Balakrishnan
SAP PM: authorisation objects
How to get the authorisation objects for SAP PM?
Check this for the common PM authorisation objects:
- I_ILOA - Change location and accounting data in the order
- I_CCM_ACT - Configuration Control authorization object
- I_ALM_ME - Mobile Asset Management
- I_VORG_MEL - PM/QM: Business Operation for Notifications
- I_QMEL - PM/QM: Notification Types
- I_BEGRP - PM: Authorization Group
How to send mails from SAP
The Details that are required before configuration.
It is required to configure SAPconnect settings for every client that is used for send processes (E-mails, Faxes, SMS).
- SMTP Mail Server Domain Name
- SMTP Port Number (usually 25).
Deploy SAP GRC
The goal of the presentation includes the following:
- Providing clear recommendations and guide the setup of customer landscapes
- Outlining the main important aspects to be considered
- Elaborating the best considered trade-off between flexibility and simplicity
- Alternative deployment options might have different benefits
- Customer individual assessment not be compensated
This presentation is divided into the following two sections:
- Solution Landscape Design Considerations This section provides an overview of aspects and questions that lead to a system landscape of a customer.
- Deployment Options for SAP solutions of Governance, Risk, and Compliance This section provides the specific deployment options for the SAP solutions of Governance, Risk, and Compliance that SAP supports. All presented deployment options represent the productive stage of a three-tier landscape.
Dependent on the targeted use cases there are different possibilities, how to design the system landscape for SAP BusinessObjects governance, risk, and, compliance (GRC) solutions. This presentation provides clear recommendations and guides the setup of customer landscapes by outlining the main important aspects to be considered. It recommends landscape setups for the SAP BusinessObjects GRC solutions based on the established methodology of SAP's System Landscape Governance Board.
Some abbreviations of the document:
- AC SAP BusinessObjects Access Control
- HR Human Resources
- BS7 SAP Business Suite 7
- LOB Line of Business, e.g. Human Resources, Sales
- BS7i10 SAP Business Suite 7 Innovations 2010 including, for example, SAP ERP EHP 5, SAP CRM EHP 1
- NFE SAP BusinessObjects Nota Fiscal Eletrônica
- BS7i11 SAP Business Suite 7 Innovations 2011 including, for example, SAP ERP EHP 6, SAP CRM EHP 2
- NW SAP NetWeaver
- BW SAP NetWeaver Business Warehouse
- PC SAP BusinessObjects Process Control
- ECC SAP ERP Central Component
- PI SAP NetWeaver Process Integration
- EHP Enhancement Pack
- RM SAP BusinessObjects Risk Management
- EP SAP NetWeaver Enterprise Portal
- SCM Supply Chain Management
- FI AP/AR Financials Accounts Payable/Accounts Receivable
- SLA Service Level Agreement
- GRC SAP solutions for Governance, Risk, and Compliance
- SP Support Package
- GTS SAP BusinessObjects Global Trade Services
- TM SAP Transportation Management
Download
- Unirte a la lista #1 de SAP +1, sumate ahora!
- Dale "me gusta" a nuestra página de Consultoria-SAP en Facebook.
Y no te olvides de seguirnos en las redes sociales para no perderte ninguna novedad: - Copia la URL de éste artículo, e ingresa al foro de Ayuda SAP en español, ve a la parte de Manuales-SAP, y abre un tema nuevo explicando por qué te interesa aprender más sobre SAP, pega ahí la URL que has copiado, para que sepamos que estás cumpliendo estos tres puntos.
Recuerda que en nuestra comunidad de Ayuda SAP no es solo "pedir" y nada más, lee las normas de solicitudes que tendrás que cumplir para descargar gratis.
No te pierdas los beneficios de ser VIP en Consultoria-SAP
Más información
Security tables
Table Description Reports
- USR02 Users Data (logon data) RSUSR020
- USR04 User master authorization (one row per user)
- UST04 User profiles (multiple rows per user)
- USR10 Authorisation profiles (i.e. &_SAP_ALL)
- UST10C Composit profiles (i.e. profile has sub profile)
- USR11 Text for authorisation profiles
- USR12 Authorisation values RSUSR030
- USR13 Short text for authorisation
- USR40 Tabl for illegal passwords
- USGRP User groups
- USGRPT Text table for USGRP
- USH02 Change history for logon data
- USR01 User Master (runtime data)
- USER_ADDR Address Data for users
- AGR_1016 Role and Profile RSUSR020
- AGR_1016B Role and Profile
- AGR_1250 Role and Authorization data
- AGR_1251 Role Object, Authorization, Field and Value RSUSR040
- AGR_1252 Organizational elements for authorizations
- AGR_AGRS Roles in Composite Roles
- AGR_DEFINE To See All Roles (Role definition) RSUSR070
- AGR_HIER2 Menu structure information - Customer vers
- AGR_HIERT Role menu texts
- AGR_OBJ Assignment of Menu Nodes to Role
- AGR_PROF Profile name for role
- AGR_TCDTXT Assignment of roles to Tcodes
- AGR_TEXTS File Structure for Hierarchical Menu – Cus
- AGR_TIME Time Stamp for Role: Including profile
- AGR_USERS Assignment of roles to users
- USOBT Relation transaction to authorization object (SAP)
- USOBT_C Relation Transaction to Auth. Object (Customer)
- USOBX Check table for table USOBT
- USOBXFLAGS Temporary table for storing USOBX/T* chang
- USOBX_C Check Table for Table USOBT_C
- TSTCA Transaction Code, Object, Field and Value
More User/Security tables
- DEVACCESS Table of development users including dev access key
- USR02 Logon data
- USR04 User master authorization (one row per user)
- UST04 User profiles (multiple rows per user)
- USR10 Authorisation profiles (i.e. &_SAP_ALL)
- UST10C Composit profiles (i.e. profile has sub profile)
- USR11 Text for authorisation profiles
- USR12 Authorisation values
- USR13 Short text for authorisation
- USR40 Tabl for illegal passwords
- OBJT Authorisation objetc table
Security Reports
SAP Security Report Name Description
- RSUSR_SYSINFO_ROLE (YOU NEED TO LOG ON TO THE CENTRAL SYSTEM FOR THIS) Report cross-systm information/role STANDARD SELECTION, User name, Receiving system, SELECT ROLE Role
- RSUSR_SYSINFO_PROFILE (YOU NEED TO LOG ON TO THE CENTRAL SYSTEM FOR THIS) Report cross-systm information/profile STANDARD CRITERIA User Name, Receiving system, Profile
- RSUSRSUIM Same as SUIM User Information System
- RSUSR402 Download user data for CA manager from Secude
- RSUSR300 Set External Security Name for all Users
- RSUSR200 List of Users According to Logon Date and Password Change
- RSUSR102 Change Documents for Authorizations
- RSUSR000 Currently Active Users Tcodes SU04 and AL08
- RSUSR002 Users by Complex Selection Criteria (search by User, Group, User Group, Reference User, User ID Alias, Role, Profile Name, Tcode, SELECTION BY FIELD NAME, Field Name, SELECTION BY AUTHORIZATIONS Authorizatrion Object, Authorization, SELECTION BY VALUES, Authorization Object 1, AND Authorization Object 2, AND Authorization Object3, ADDITIONAL SELECTION CRITERIA, Account number, Start Menu, Output Device, Valid Until, Locked Users ONLY, Unlocked Users Only, CATT Check ID
- RSUSR002_ADDRESS Select User According to Address, NAMES, First Name, Last Name, User, COMMUNICATION PATHS, Company, City, Buildings, Room, Extension, OTHER DATA, Department, Cost Center
- RSUSR003 Check the Passwords of Users SAP* and DDIC in All Clients (SAP* DDIC SAPCPIC )
- RSUSR004 Restrict User Values to the following Simple Profiles and Auth Objs SELECTION CRITERIA Single Profiles, Authorization Objs
- RSUSR005 List of Users with Critical Authorizations (SAME AS RSUSR009 but difference is here you can't chose)
- RSUSR006 List of Users According to Logon Date and Password Change
- RSUSR007 List Users Whose Address Data is Incomplete (here give the Required Address Data)
- RSUSR008 Critical Combinations of Authorizations at Transaction Start (Can view either Critical Combinations or Users)
- RSUSR009 List of User with Critical Authorizations SAME AS RSUSR005 but here you can (Check using either customer data of Check using SAP data
- RSUSR010 Transaction for User with Profile or Authorization (Transaction executable either by, User, with Role, Profile, Authorization
- RSUSR011 Lists of transactions after selection by User, profile or obj SELECTION FOR User
- RSUSR012 Search authorizations, profiles and users with specified object value (DISPLAY authorization objects, DISPLAY authorizations, DISPLAY profiles, DISPLAY users)
- RSUSR020 Profiles by Complex Criteria SELECTION CRITERIA Profile, Profile test, ADDITIONAL CRITERIA FOR PROFILES, Composite Profile, Single Profile, Generated Profiles, SELECTION BY CONTAINED PROFILES Profile, SELECTION BY AUTHORIZATIONS, Authorization Object, Authorization, SELECTION BY VALUES, Auth obj, auth obj2, auth obj3, SELECTION BY ROLE
- RSUSR030 Authorizations by Complex Selection Criteria SELECTION CRITERIA, Auth Object, Authorization, BY VALUES
- RSUSR040 Authorization Objects by Complex Criteria, STANDARD SELECTIONS, Authorization object, ADDITIONAL CRITERIA Object class, Obj class text, Field
- RSUSR050 COMPARISIONS, Compare Users, USER A ------** USER B--------, ROLES, PROFILES< AUTHORIZATIONS, Across Systems
- RSUSR070 Roles by Complex Selection Criteria STANDARD SELECTION Role, Description, SELECTION BY USER Assignments
- RSUSR100 Change Documents for Users
- RSUSR101 Change Document for Profiles
More info: https://answers.sap.com/questions/1294267/security-reports.html
Difference between SAP areas
Question:
Hi, I am a recruiter and would like to know what is the difference between these 3: SAP Developer, SAP Technical Consultant and SAP Techno Functional Consultant. Would highly appreciate a reply from you.
Broadly, there are 3 areas in SAP [ There can be several other sub-categories ]:
- Functional [ like MM/PP/SD ] : Related to business processes and configuration
- Development [ also called technical or ABAP or Netweaver programming ]: Related to programming
- Basis/Netweaver/SAP/Technical admin : related to system installation and support
a.) SAP developer is related with 2.
b.) SAP Technical consultant is related with 2 and can also be referred for 3. So you need to check the requirement in details and ensure which one is being referred. It also indicates a higher level of expertise and experience in the field compared to a.)
c.) Techno-Functional is someone with experience in both development [programming ] as well as functional areas. Generally, these are the consultants with
a lot of experience in development and by virtue of working with functional consultants and users, they've also acquired skills in business process and config [ functional ] side.
In any case, for your purpose you should look into details of a consultant's CV and try to match with the resourcing-requirement document.
So it seems that recruitment consultants are now getting serious about their job and trying to understand what business needs. They usually rely on word-matching between resourcing requirement document and consultant's CVs.
Source: Sapblog.rmtiwari.com
Links to Upgrade SAP Solution
Preparing to upgrade your SAP solution?
If so, here’s a list of useful links; you would need to review and study in depth to make your upgrade successful.
- service.sap.com/upgrade - SAP Upgrade Info Center
- service.sap.com/upgradenewsletter - SAP Upgrade Experience Database
- service.sap.com/goinglive-fu - SAP GoingLive Functional Upgrade Check
- service.sap.com/upgradeservices - Upgrade Services
- service.sap.com/upgradetools - Tools to support the upgrade execution from a technical and functional perspective
- service.sap.com/upgraderoadmap - Central Guidance to Planning and Execution of an SAP Upgrade Project
- service.sap.com/upgradedb - SAP Upgrade Experience Database, custumer's upgrade experiences
- service.sap.com/safeguardingupgrade - Holistic Engagement for Technical Risk Mitigation in SAP Upgrade Projects
- service.sap.com/ufg - SAP Upgrade Focus Group
- service.sap.com/upgrade-bi - SAP NetWeaver Business Intelligence
- service.sap.com/upgrade-erp - SAP ERP Upgrade
- service.sap.com/upgrade-crm - SAP CRM Upgrade
- service.sap.com/upgrade-srm - SAP SRM Upgrade
- service.sap.com/upgrade-scm - SAP SCM Upgrade
- service.sap.com/upgrade-nw - SAP NetWeaver Upgrade
- forums.sdn.sap.com - SDN Upgrade Discussion Forum
Source: SapPort.Blogspot.com
SAP GUI – A platform of/for change ?
The OldSAP GUI has been used since the early days of R2. It has evolved over the years from simple software with minimal graphical elements to a customizable Windows vista based graphical user interfaces.
Around the globe more than 50,0 00 customers worldwide run SAP. Just about everyone is this list uses SAPGUI. Hence it’s a given that the install base for SAP GUI is immense.
SAPGUI is a given, a silent performer who always did his work diligently but could never outshine its partner, a powerhouse called SAP ERP.
Are there any interesting ways to use the install base for SAP GUI and spice up things in this old guy’s life?
The newThe last couple of years have made Web 2.0 and some of its related concepts extremely popular. Many of these concepts are primarily based on empowering the user. Giving them control to choose what they want, giving them access to customize what they want, giving them everything and letting content get generated etc., Widgets is a small sidetrack ,an experiment in this area.
Everyone likes widgets, but widgets never took off, for a variety of reasons. They required a separate widget engine to run, they did not do anything useful, after a few days/weeks the novelty wears off and they could never reach a critical user base to go mainstream. But anyone who has tried it will tell you that they are handy. Widgets are micro apps developed for a particular purpose, usability is excellent, they are right there in the desktop and majorly use push technology (perhaps an under rated feature).
Mix them allNow, let us imagine this. SAP GUI has an excellent install base; it enables business users to work on tasks which have direct implications to their business. Make this GUI as a widget engine, where users can pick transactions as widgets and load them on the desktop.
Suddenly those pretty looking widgets become a powerhouse of activity. Making SAP GUI as a widget engine will help users launch only that content which they require. When combined with SNC features, they are secure. This combination leverages each other’s strengths and creates a product which fits neatly into this web 2.0 world. SAP GUI will get a major face lift and change the way customer perceive SAP applications.
Since it uses the same engine, widgets would be fast to load and if we get it right, someday a simple WD ABAP based time sheet application will be sitting in your desktop as a widget.
Now who wouldn’t want to enter fill his time-sheet before leaving office?
On a technical front, SAP GUI uses TCP/IP, client server based and works primarily as a pull technology. An implementation of this sort would require some major modifications in the core, making it sort of a rich client, but it would be an interesting step forward. As an optimist I like to think it’s a step which has positive effects. Who knows , interesting widgets developed using this might someday reduce the need for composites.
Bharathwaj Ragothaman Bharathwaj works with SAP Global Delivery.His job role involves providing consulting services for implementations on Portals,PI,SOA, BPM and various UI technologies from SAP.He is a SAP certified PI and EP consultant.
Reblogged from SDN.sap.com
ABAP External Debugging
El artículo había sido publicado por SAP.com y ahora ha sido eliminado, por lo tanto no se veían las capturas que incluíamos. Hemos eliminado las capturas porque daban error. Mantenemos la info compartida a fines educativos. Disculpen las molestias.
ABAP External Debugging - New User Breakpoint
1. Motivation
The user breakpoint in ABAP helps you to debug the ABAP components of applications, that use RFC- and HTTP- based communications. These could be Web Dynpro applications, BSP's, ABAP-based web services, RFC-enabled function modules and so on. By setting a user breakpoint you can interrupt the processing of external HTTP or RFC requests in your ABAP backend system and debug them.
You can set a user breakpoint in the Object Navigator (transaction SE80) or the ABAP Editor (transaction SE38). Before you set a user breakpoint you may want to specify the user to whom the breakpoint applies. By default your user is set. You can enter the user in the User field of the debugging settings dialog (Utilities->Settings->Debugging). Before you start debugging, make sure that you use the New ABAP Debugger (select the checkbox New Debugger ). Now HTTP or RFC requests can be sent to your ABAP backend system - you are ready to capture them for debugging.






![CSAP1: índice del curso SAP [ebook] CSAP1: índice del curso SAP [ebook]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhf5uioeX9uaZsZIUUVs7MLohe6Vs4oddfPBRlo_ON8FZ4UwAOtjxlwH-c1YIOC28-XTnig7oLXN67-YLwvmXgpGD8XDT7e-rzkXOBoaMHe1HI3qjSqkLiG8vRADJqJIsRR6ffONrKWmZen/s72-c/)